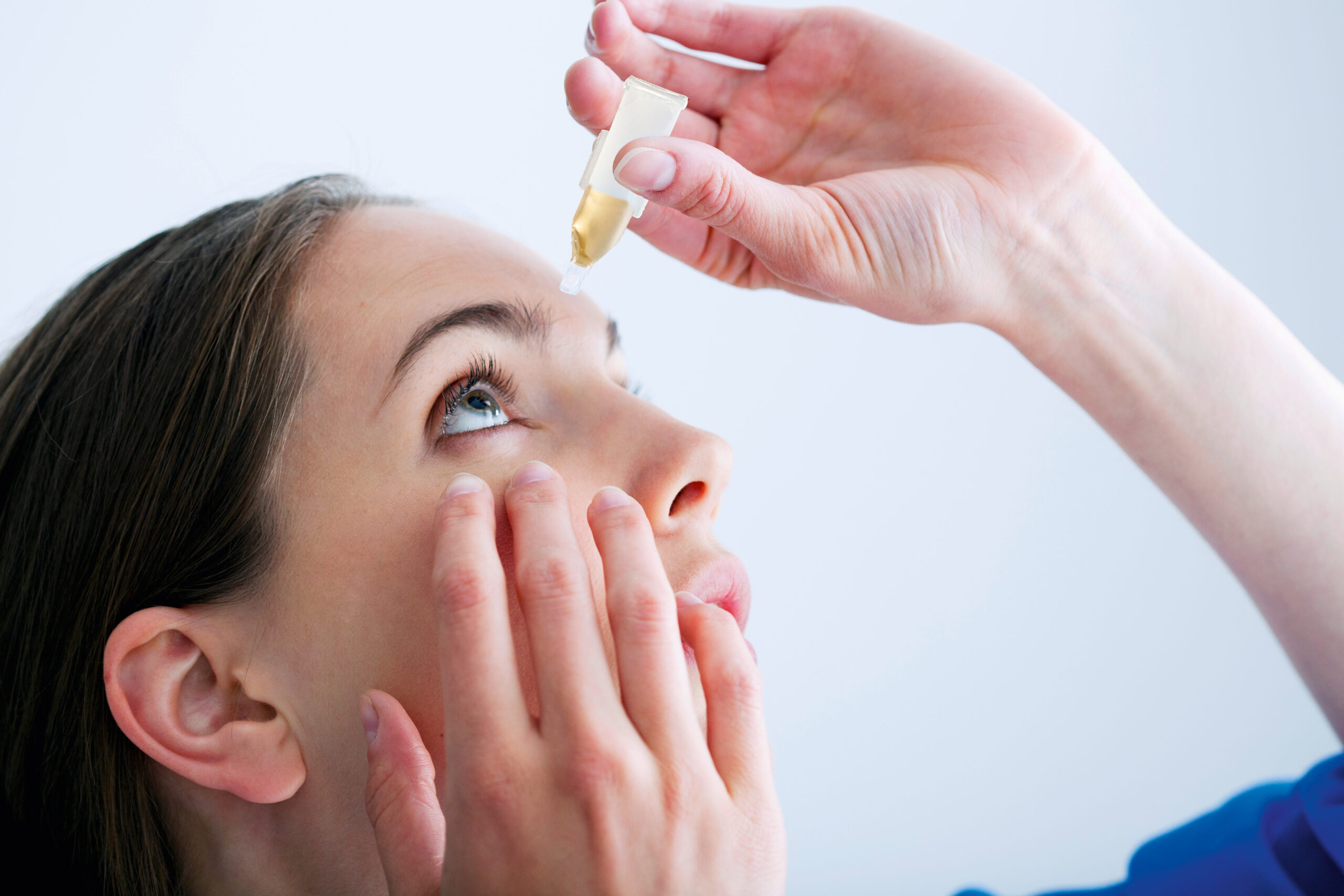
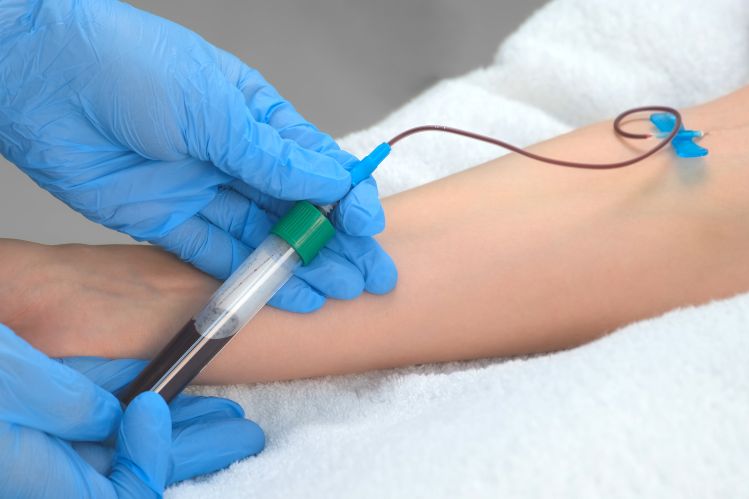
In modern ophthalmology, serum eye drops offer a valuable treatment option for patients with various eye surface disorders, such as dry eye or severe corneal problems. These drops are derived from blood and offer a natural and effective alternative to conventional tear substitutes. There are two main types of serum eye drops: autologous and allogeneic. This article explains the differences between the two and their respective advantages and applications.
„Both autologous and allogeneic serum eye drops are safe and show positive effects in patients with ocular surface diseases.“1
„
Autologous serum eye drops
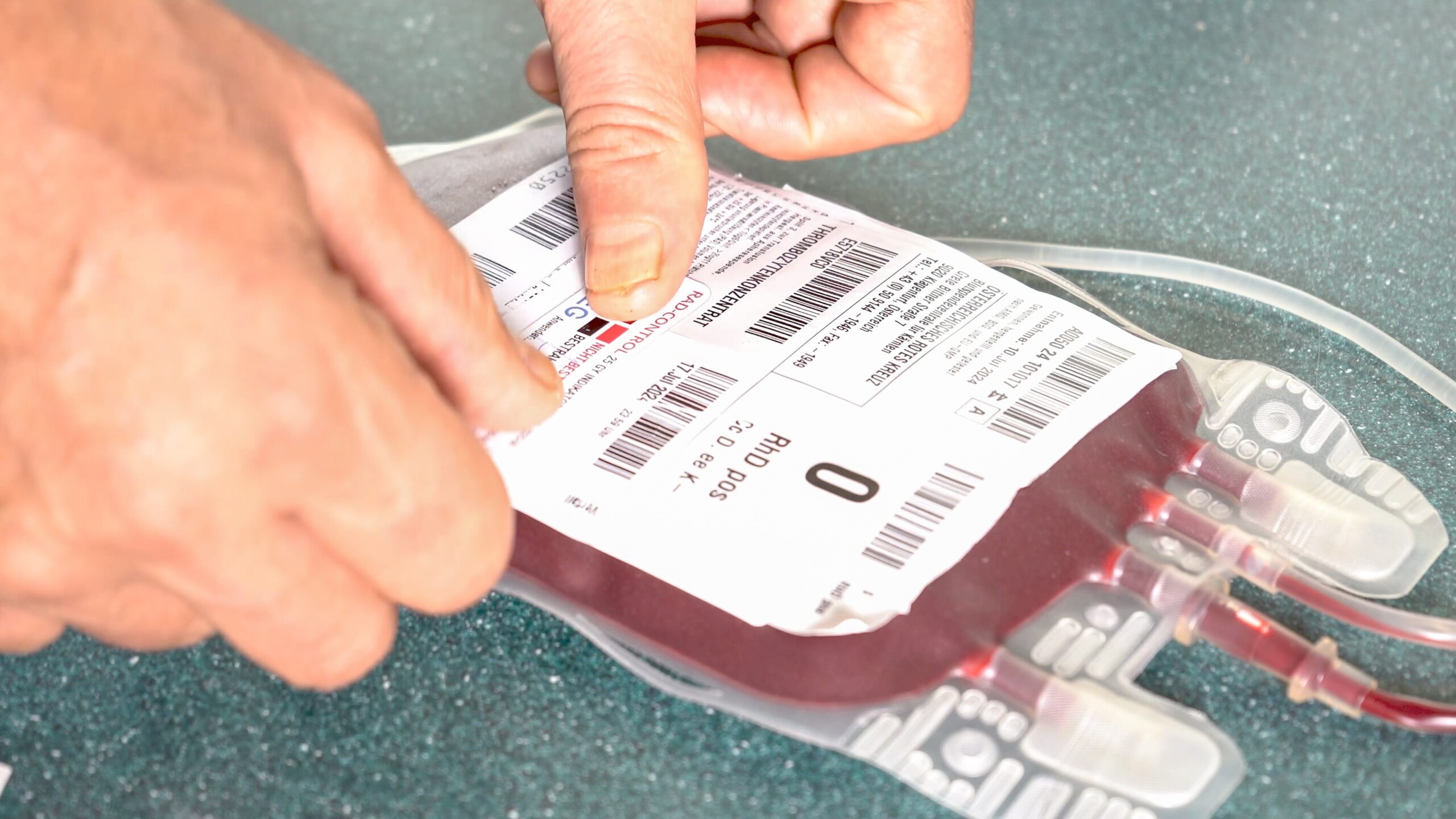
Autologous serum eye drops are made from the patient’s own blood. The process begins with a blood sample, in which a certain amount of blood is taken. This blood is then centrifuged to separate the serum. The serum obtained is then processed into eye drops, e.g. using the automated Jetrail® system.
Advantages of autologous serum eye drops:
- Biocompatibility: Since the drops are made from the patient’s own blood, the risk of an allergic reaction or rejection is minimal.2
- High content of growth factors and nutrients: These drops contain important proteins, vitamins and growth factors that promote healing and regeneration of the eye surface.3
Application: Autologous serum eye drops are used for severe diseases of the ocular surface. These include advanced forms of dry eye, immunological rejection reactions after bone marrow or stem cell transplants, and severe chronic inflammation or damage to the conjunctiva and cornea as a result of chemical burns or burns. In many of these cases, serum eye drops are often the only effective treatment option when conventional approaches are no longer sufficient.4
Allogeneic serum eye drops
Unlike autologous serum eye drops, which are obtained from the patient’s own blood, allogeneic serum eye drops are produced from the blood of a donor. This method is used when the patient is unable to donate their own blood or when a larger amount of serum is required.
Advantages of allogeneic serum eye drops:
- Availability: Allogeneic serum eye drops can be produced more quickly and in larger quantities because they do not rely on the patient’s own blood.
- Practicality: Allogeneic drops offer a practical alternative for patients who cannot have blood taken due to their health condition.
- Safety: Allogeneic serum eye drops are manufactured according to strict criteria – for example, blood donors are screened for infectious diseases, medications and other risk factors.5
Application: Allogeneic serum eye drops are used similarly to autologous drops in the treatment of eye surface diseases. They are particularly useful in situations where the timely availability of serum drops is crucial.
Which serum eye drops are more effective?
Both autologous and allogeneic serum eye drops are effective treatment options for diseases of the ocular surface. In a randomised, double-blind crossover study, the therapeutic effect of both types of drops was directly compared.
The results show that autologous serum eye drops are slightly more effective in terms of symptom improvement and tear film stability. Nevertheless, both forms of therapy were assessed as safe and effective, especially for persistent corneal defects and severe dry eye.
Allogeneic drops also offer advantages in terms of availability and for patients who are unable to donate their own blood.6
What does the future hold?
The economic relevance of autologous and allogeneic serum eye drops differs significantly due to their production processes and scalability. Autologous serum eye drops, which are produced individually from the blood of each patient, require personalised and time-consuming procedures, which increases production costs. This individualised approach also limits scalability and leads to higher costs per unit. In contrast, allogeneic serum eye drops can be produced in larger batches from donated blood, enabling more efficient use of resources and greater production capacity. These economies of scale reduce the production costs per unit and make allogeneic serum eye drops a more economically attractive option for widespread use. This standardisation allows allogeneic drops to be delivered more quickly and cost-effectively, increasing their availability and economic efficiency compared to autologous drops. From an economic perspective, a trend away from autologous to allogeneic serum eye drops is therefore obvious.
Sources:
1 Übersetzung des Originals aus van der Meer P. et al., Acta Ophthalmologica, 99(8), 2021, S. 837–842. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/aos.14788.
2 Geerling G., Hartwig D., Wedel T., Epitheliotrophic capacity of serum and plasma eyedrops. The Ocular Surface, 18(2), 2020, 223–231.DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtos.2020.03.001.
3 Schindler T., Autologous Serum Eye Drops for Dry Eye. Healthline, 2023.
URL: https://www.healthline.com/health/chronic-dry-eye/autologous-serum-eye-drops-for-dry-eye.
4 DRK-Blutspendedienst, Bei schweren Augenerkrankungen hilft ein Serum aus dem eigenen Blut. blutspende.de, 2023. URL: https://www.blutspende.de/magazin/von-a-bis-0/bei-schweren-augenerkrankungen-hilft-ein-serum-aus-dem-eigenen-blut.
5 van der Meer P., Verbakel S. K., Honohan A., Lorinser J., Thurlings R. M., Jacobs J. F. M., de Korte D., Eggink C. A. Allogeneic and autologous serum eye drops: a pilot double-blind randomized crossover trial. Acta Ophthalmologica, 99(8), 2021, 837–842. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/aos.14788.
6 van der Meer P., Verbakel S. K., Honohan A., Lorinser J., Thurlings R. M., Jacobs J. F. M., De Korte D., Eggink C. A. Allogeneic and autologous serum eye drops: a pilot double-blind randomized crossover trial. Acta Ophthalmologica, 99(8), 2021, 837–842. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/aos.14788.
Authors: Dr. Harald Sekljic, Dr. Clemens Troschl, Lisa Springer